Environment
Overview
Environment defines the "studio" setting in which the composing happens on the planner. The background properties and lighting all affect how the product is presented. We have decided that the product is the highlight of the base scene, therefore are by default providing a very basic, minimalistic environment.
Environment properties are found in : Site Configuration > [Site name] > Configuration appearance > 3D Environment
You can change the environment through the following parameters.
Environment Map
| Property Name | Type | Localized | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| EnvironmentMapAssetId | HDR Asset | N/A | The HDR asset linked. Refer to Environment Map for more information |
| EnvironmentMapIntensity | Number | N/A | The intensity of the map's light its emitting |
Background
Transparent
This option will make the scene's background, transparent.
Skybox
This is a property of the environment that becomes active if the selected background option is: "Skybox" See SkyBox for more informations.
| Property | Type | Localized | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SkyBoxAssetId | HDR Asset | N/A | The Skybox asset that is linked to environment. |
Solid
This will fill the scene background with a uniform color.
Gradient
The gradient will fill the scene with a three color gradient. you can select the top, horizon and bottom colors.
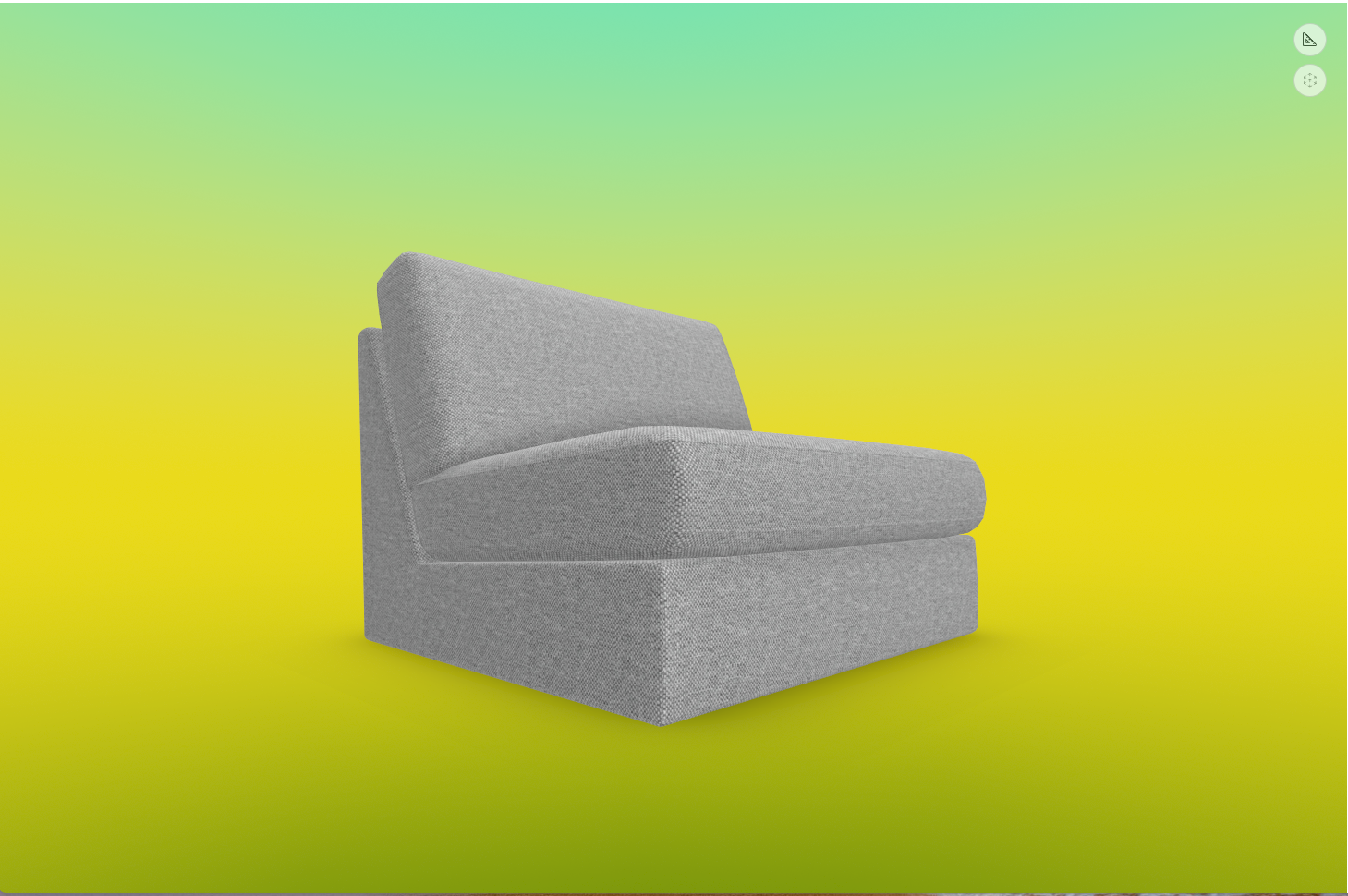
Example of how gradient will appear in the 3D scene:

Light
Describing the behavior of the light: color and intensity
| Property Name | Type | Localized | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color | RGB color | N/A | The color the light emits |
| Intensity | Number | N/A | The intensity of light emitter, higher values indicate stronger light |
Tone Mapping
| Property Name | Type | Localized | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ToneMapping | Radio button | N/A | The type of tone mapping applied to environment: EnablePanning, NoToneMapping, LinearToneMapping, ReinhardToneMapping, CineonToneMapping, ACESFilmicToneMapping, AgXToneMapping, NeutralToneMapping |
Note
Tone Mapping is a technique used in computer graphics and image processing to convert high dynamic range (HDR) imagery to a format displayable on standard low dynamic range (LDR) monitors and screens.
NoToneMapping - Disables tone mapping entirely, displaying raw HDR values without any compression or adjustment. LinearToneMapping - Simple linear scaling that uniformly reduces brightness values by a constant factor. ReinhardToneMapping - Classic tone mapping that compresses highlights while preserving midtones, creating natural-looking results with smooth rolloff. CineonToneMapping - Film-based tone mapping that mimics traditional Kodak Cineon film response curves for cinematic color grading. ACESFilmicToneMapping - Industry-standard tone mapping based on the Academy Color Encoding System, providing filmic contrast and color reproduction. AgXToneMapping - Modern tone mapping algorithm designed for photorealistic rendering with improved highlight retention and color accuracy. NeutralToneMapping - Balanced tone mapping that aims to preserve the original image appearance while fitting within display ranges.
Camera
| Property Name | Type | Localized | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| EnablePanning | Toggle | N/A | Toggle to define if Camera can be panned or not |
| MinDistance | Number | N/A | The minimum zoom distance from the center in meters |
| MaxDistance | Number | N/A | The maximum zoom out distance from the center in meters |
| MinVerticalAngle | Number (degrees) | N/A | Camera control limiting angle of view. Negative values permit looking up from below |
| MaxVerticalAngle | Number (degrees) | N/A | Camera control limiting angle of view. 90 degrees is directly from above |
| CentralHorizontalAngle | Number (degrees) | N/A | The default horizontal camera angle. 0 is directly at front, where X-axis points right, Y-axis up and Z-axis forwards. This is used in conjunction with MaxHorizontalAngle to limiting rotation around the product. |
| DefaultCameraAngle | Vector2 (degrees) | N/A | The default camera angle in degrees, represented as a Vector2 where X is the horizontal angle and Y is the vertical angle. |
| MaxHorizontalAngle | Number (degrees) | N/A | Camera control limiting angle of view. 0 means camera can't be rotated horizontally. 90 allows half-sphere rotation, but does not allow going behind the product. Values equal and above 180 mean that the camera can be freely rotated around the product. |
| FieldOfView | Number (degrees) | N/A | Camera 'view' field of view in degrees, wider FOV permits broader view. This acts similarity than real camera field of view parameter and will affect how perspective behaves on the scene |
Note
DefaultCameraAngle is used when initially opening a planner or when resetting the camera. This value should be within the range defined by CentralHorizontalAngle/MaxHorizontalAngle constraints for X axis and by Min/Max VerticalAngle for Y axis. Values outside these ranges will trigger a runtime data generation warning. The X-axis validation must be between (CentralHorizontalAngle - MaxHorizontalAngle) and (CentralHorizontalAngle + MaxHorizontalAngle).
Ambient Occlusion
Ambient occlusion (AO) is a shading technique used to simulate the soft shadows that occur in crevices, corners and areas where surfaces meet, enhancing the perception of depth and adding realism to 3D scenes. It works by darkening areas that are less exposed to ambient light, mimicking the subtle shading observed in real-world environments.

| Property Name | Type | Localized | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity | Number | N/A | Controls the strength of the ambient occlusion (AO) effect when it's blended with the original scene rendering. |
| Radius | Number | N/A | Updates the GTAO (Ground Truth Ambient Occlusion) material's radius parameter, which defines the sample radius used to calculate occlusion. |
Note
Blend Intensity Usage: Adjusting this value allows you to fine-tune how pronounced the ambient occlusion appears in your scene, enabling subtle shading or more dramatic shadowing effects.
Note
Radius Impact: A smaller radius focuses the occlusion effect around nearby surfaces, leading to sharper shadows in tight areas. A larger radius extends the effect over a broader area, resulting in softer, more diffused shadows.